Article Legend
All future posts will include a rating indicating their potential clinical importance.
These ratings will be:
A – Very important and ready for consideration
B – Clinically important for future consideration
C – May become important in the future
D – Related to neurobiology or theory
We’re back!
After a pandemic-related hiatus, we’re back, and we hope to bring you articles regularly. For print subscribers, we hope to send out a single large issue in the coming months.
“Epigenetic Changes After Trauma May Be Adaptive, Contribute to Resilience”
Originally From Psychiatric News Update
In recent years, research throughout the scientific and medical community has suggested a link between trauma and epigenetic changes, chemical modifications that affect gene activity without actually changing the gene’s DNA sequence. The assumption has been that epigenetic changes in the context of trauma are inherently bad, a form of damage that gets passed from generation to generation. But according to Rachel Yehuda, Ph.D., Endowed Professor of Psychiatry and Neuroscience of Trauma at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, these changes may also be adaptations that promote resilience.
“Sometimes the biological changes in response to trauma or intergenerational trauma are there to help deal with the problem of trauma, not compound its effects,” Yehuda said. “The survival advantage of this form of intergenerational transmission depends in large part on the environment encountered by the offspring themselves.”
Yehuda described this phenomenon as a paradox.
“Parental or ancestral trauma may heighten vulnerability to mental health challenges, but epigenetic adaptations may simultaneously facilitate coping mechanisms,” she said. “Trauma increases susceptibility for psychological distress, but also produces adaptations that help us cope with them.”
Yehuda described research she and her colleagues have conducted to tease out how trauma in parents can affect offspring in the context of the biology of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in Holocaust survivors and their children. As the research unfolded, Yehuda and colleagues found that survivors’ adult children were more likely to have mood disorders, anxiety disorders, and PTSD than Jewish people whose parents did not directly experience the Holocaust. This was especially true of children of Holocaust survivors who had PTSD. The researchers also found that many children of Holocaust survivors had low levels of the stress hormone cortisol, particularly if their parents had PTSD.
Yehuda and colleagues then conducted a series of studies that looked at the role of glucocorticoid receptors — the proteins to which cortisol must bind to exert its effects — and found evidence that these receptors were more sensitive in people with PTSD.
“In practical terms this means that even though someone with PTSD might have lower circulating levels of cortisol in their blood, their cells might react more strongly to the cortisol that is present,” Yehuda said.
Yehuda said that epigenetics provided further insight on the relationship between hypersensitive glucocorticoid receptors, cortisol, and PTSD. She explained the potential role of methylation, which is a chemical reaction in the body in which a small molecule called a methyl group gets added to DNA or DNA-associated proteins.
“Increased methylation generally impedes RNA transcription, whereas less methylation enhances gene expression,” Yehuda said.
In 2015, Yehuda and colleagues conducted a study involving combat veterans who had PTSD and found lower methylation on an important region on the participants’ glucocorticoid receptor gene. The changes were associated with cortisol and glucocorticoid receptor sensitivity in the study participants, suggesting a potential epigenetic explanation for the association between the trauma of combat and PTSD.
Yehuda said that stress-related epigenetic changes may be reversible. For example, one of the studies conducted by her team revealed that combat veterans with PTSD who benefited from cognitive-behavioral psychotherapy showed treatment-induced changes in the methylation of a gene that regulates glucocorticoid receptor sensitivity. Yehuda said that this finding confirmed that healing is also reflected in epigenetic change.
“That we can transform to meet environmental challenge is a superpower. That is resilience,” Yehuda said.” ?
Yehuda then went on to describe the striking and lasting effects of the psychedelics psilocybin and MDMA in trauma and in helping patients confront their fears in a positive and hopeful fashion. These agents which are given with intensive psychotherapeutic support are not yet FDA approved, but preliminary data suggest that they can have dramatic therapeutic effects in trauma and depression. They can help patients change their attitudes to themselves and the world.
Lithium vs Anticonvulsants Lamotrigine and Valproate on 10 year physical illness
In a study by lars Kessing in (European Neeuropsychopharmcology Volume 84, July 2024, Pages 48-56) on 169,285 patients taking either lithium or the anticonvulsants Lamotrigine (LTG) or Valproate (VPA) for at least 10 years, there was no difference in physical outcome in any physical outcome, including chronic kidney disease, except for a higher incidence of myxedema.
Other diagnoses that showed no difference included stroke, arteriosclerosis, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis, dementia, Parkinson’s disease, chronic kidney disease and cancer (including subtypes).
Editors Note: This data further supports an already robust existing literature that lithium is not more likely to cause chronic kidney disease or other physical illnesses than other anticonvulsant treatments with the exception of hypothyroidism. Patient should be made aware of these and the related long term data that lithium is no more likely to cause chronic kidney disease than other treatments and, in some cases, these other treatments cause more end-stage renal failure. The misapprehension that lithium is more toxic than other treatments has led to the vast underutilization of this treatment. Lithium is the treatment of choice for bipolar illness and should be used earlier, more often, and more persistently. When this is done illness outcomes and patient’s well being are significantly improved.
Quotes from Kay Jamison, PhD, Professor of Psychiatry at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine
“There’s this notion that mania and depression are uncommon or certainly that mania is uncommon, and that is not true. The bipolar illness spectrum is associated with a lot of very damaging things, most importantly suicide, but also alcohol and drug use and violence. It’s a very early onset illness, so unlike dementia or heart disease, which hit people much later in life, these hit people when they’re young. They have to cope with [bipolar disorder] when they’re young, and they don’t have the experience of life to help them out. That tends to be overlooked, what it does to people and their families, and how devastating it is. First and foremost, I would want people to know that it’s treatable, imperfectly treatable, but treatable, and it’s important to get it treated….It’s completely reasonable to extend hope to somebody who has bipolar illness but to also make it very clear that it’s hard. But draw upon what you know. Read, read, read. Learn about it. Badger your doctors. Why are they doing this? What’s the point of this drug rather than that drug? Always question what’s happening to you. “
Editor’s Note: One of the most important things that people with mood disorder can do, is to every night chart chart their mood, functioning, sleep, medications, and other symptoms so that this graphic longitudinal assessment can be shown to their physician/therapist at each visit. This will help most efficiently refining the treatment regimen for an optimal long term outcome. See www.bipolarnews.org (click on Personal Calendar or Life Chart) for a good format for doing these daily ratings.
Parents of children (age 2-12) with mood and behavioral disorders can each week rate the severity of their child’s symptoms of anxiety, depression, ADHD, oppositional behavior, and mania on a secure website. This can be printed out to assist physicians with the assessment of need for treatment and of how well treatment is working. Informed consent for this system is available at www.bipolarnews.org (click on Child Network).
LITHIUM IS VASTLY UNDER-UTILIZED IN BIPOLAR DISORDER LEADING TO PREMATURE DEATH AND DISABILITY: WE WANT YOU TO HELP REVERSE THIS ANOMALOUS TREND
We are looking for people who have had a good course of illness with lithium included in their treatment regimen to help spread the word that lithium works extremely well and its side effects are erroneously overestimated.
We are hoping that you, as a good responder to lithium, will start a positive chain letter to fellow patients, family members, and friends suggesting that earlier and greater use of lithium would be overwhelmingly likely to improve the lives of many individuals with bipolar illness.
Why do we need you? It is because every expert in the treatment of bipolar illness of whom I am aware of has long advocated for greater and earlier use of lithium, but with little success. Lithium is widely recognized as a first line and treatment of choice for bipolar disorder, yet its use remains miniscule. In the US somewhere between only 10 to 27% of bipolar patients are given lithium. This has tragic consequences.
Treatment outcomes of the illness remain poor with vast numbers of patients experiencing pain, disability, memory loss, and loss of many years of life expectancy from suicide, cardiovascular disease, and many other psychiatric and medical disabilities. Compared to the general population, people with bipolar illness lose between 10-15 years of life expectancy. A new study by Carvalho et al (Psychother Psychosom, 2024) of more than 50,000 patients with a first episode of mania compared to more than 250,000 matched controls have a significantly higher rate of all cause mortality and a 10 fold increase of suicide. Those treated with lithium have a significantly lower rate of both all cause mortality and of suicide.
In addition, lithium has many other assets, besides the treatment of mania, of which most people are unaware and the liabilities of its side effects profile are over estimated. Some of the positive’s of lithium are listed below. Please print this ‘list of assets of lithium out and give it to everyone who might be interested. Patients with bipolar disorder should also print it out for their treating physicians, particularly if they do not as yet have lithium in their treatment regimen.
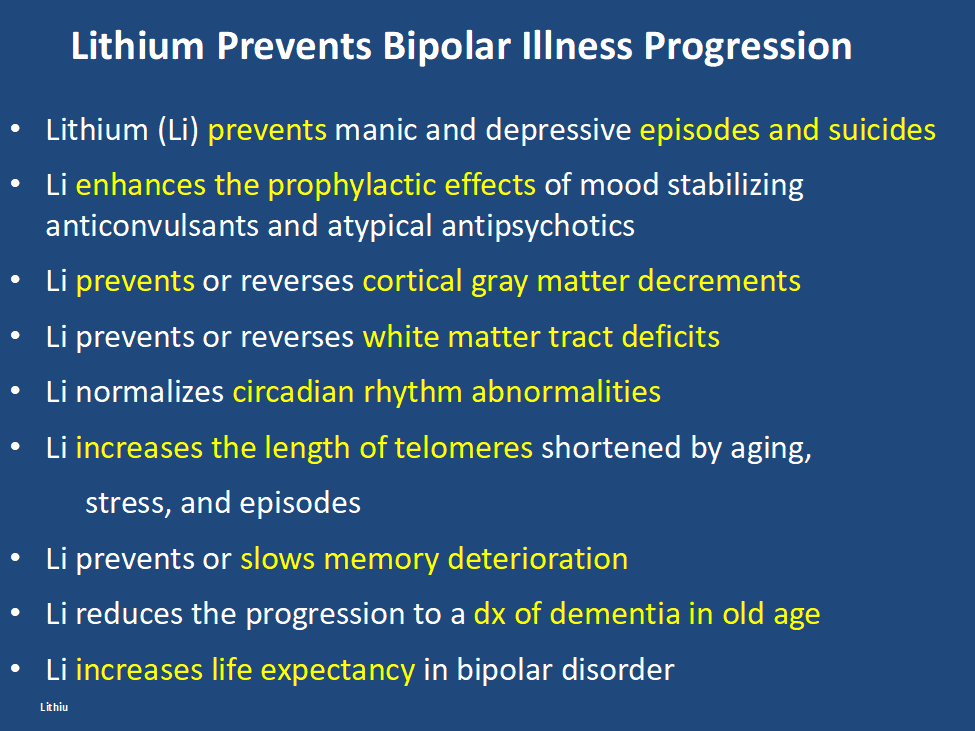
At the same time lithium’s side effects are over emphasized. The biggest concern is that lithium causes end stage kidney dysfunction eventually leading to dialysis. This is likely based on findings that individuals with bipolar disorder have an increase in most medical illnesses including chronic kidney disease compared to the general population. However, two very large trans-national studies of bipolar patients in Denmark and in Israel have found that bipolar patients treated with lithium are no more likely to get end stage renal disease than those treated with anticonvulsants such as valproate (Depakote). Lithium does cause low thyroid function in 15-25% of patients, but this is easily corrected with replacement of thyroid hormone. Many other side effects of lithium such as tremor can be managed by using lower doses.
Bottom line: Lithium gets a bad rap.
Please tell everyone you know about the new data on lithium’s relative safety and its many assets including reducing all cause mortality and suicide and restoring many years of lost life expectancy. 14 of 15 studies indicate that if lithium is started early in course of bipolar disorder it is more effective than starting it after many episodes or rapid cycling have occurred. It also works well in youngsters with bipolar disorder and better in comparison to other treatments (Hafeman et al 2020). In addition, after a first mania, patients randomized to a year of treatment with lithium do better on all outcome measures than those given a year on quetiapine (Seroquel) including manic and depressive severity, functioning, cognition, and normality of brain imaging (Berk et al 2017).
One more conceptual breakthrough: Lithium is literally the original salt of the earth. It was generated just 20 minutes after the big bang origin of the universe and is considered an essential element. Common table salt, sodium chloride, emerged only many millions of years after the big bang. Also in six studies across multiple countries, higher minute levels of lithium in the drinking water have been shown to reduce the incidence of suicide in the general population. A very low dose of lithium 150-300mg/day has also been shown to reduce the progression of mild cognitive impairment in otherwise well elderly volunteers.
Do a good thing for other people. Relay this new view of lithium to everyone you can think of in hope that they will help get the word out to many others and improve the life, functioning, and longevity of those with bipolar disorder.
Suggest and promulgate a new mantra:
“LITHIUM PREVENTS EPISODES OF BIPOLAR ILLNESS, AND PROTECTS THE BRAIN AND BODY”
Bipolar I patient show dramatic reductions in white matter integrity
Thiel et al in Neuropsychopharmacology (2024) reported that “Compared with HC [healthy controls], BD-I patients exhibited lower FA [fractional anisotropy] in widespread clusters (ptfce-FWE?< 0.001), including almost all major projection, association, and commissural fiber tracts. BD-II patients also demonstrated lower FA compared with HC, although less pronounced (ptfce-FWE?=?0.049).”
Editors Note: These data once more emphasize the importance of using lithium (Li) in bipolar disorder as it can ameliorate the deficits in white matter integrity that are so prominent in the illness. Li also improve the loss of cortical grey matter volume that evolves with illness progression. Li prevents episodes of depression and mania and reduces the incidence of suicides. That Li can reverse or ameliorate brain abnormalities in bipolar disorder is one more piece of evidence that Li should be considered a disease modifying drug (DMD) and started early in the course of illness in almost all bipolar patients. The new mantra for patients and clinicians is: Use more lithium and prevent illness progression.
GLP-1s Might Decrease the Incidence of Depression and Anxiety
Lisa O’Mary of WebMD wrote: “People taking a popular type of drug for weight loss or to manage diabetes have a lower likelihood of being newly diagnosed with depression or anxiety, according to an analysis of millions of people’s health records.
The findings were published this week by researchers from the electronic health record company Epic. Researchers looked for new diagnoses of depression or anxiety among people who started taking drugs from a class called GLP-1 agonists that can help manage blood sugar or treat obesity by mimicking hormone levels in the body that can affect appetite and blood sugar. Many people who take the drugs experience significant weight loss.
The researchers found that people with diabetes who started taking most versions of GLP-1 agonists were between 11% and 65% less likely to be newly diagnosed with depression than people with diabetes who didn’t take one of the drugs. The greatest reduction in likelihood of a new depression diagnosis was observed among people taking tirzepatide, which is sold under the brand names Mounjaro and Zepbound.”
Antidepressant Use and Risk of Manic Episodes in Children and Adolescents With Unipolar Depression
Suvi Virtanen, PhD; et al in JAMA Psychiatry. September 27, 2023. report a low risk of switching in youngsters with unipolar depression. However, the odds ratio for a switch were significantly elevated when there was concomitant use of anticonvulsants and antipsychotics, and there was a four fold increased risk if a parent had bipolar disorder. Thus one should be particularly careful about treating depression with antidepressants (AD) when there is a positive parental history of bipolar disorder and one should think of other options, such as lamotrigine, an atypical with good AD effects, or lithium.
Smoking Pot While Pregnant is a No-No
Mom, Don’t Think Smoking Pot When Pregnant is Harmless for your Child
In a new article in Science, Jasmine Hurd reports on a large sample of mothers who smoked pot while pregnant. Their offspring were more anxious, hyperactive, and aggressive and had higher levels of the stress hormone cortisol in their hair at ages 3-6.
When Superstorm Sandy hit, mothers who were stressed and smoked pot while pregnant had children 31 times more like to have oppositional defiant disorder and 7 times more likely to have an anxiety disorder. Stress may interact negatively with the effects of pot.
In fetuses aborted after being exposed to pot while in utero had decreased dopamine receptors in the their amygdala and n. accumbens, a reward center in brain. In animal studies, pregnant mother rodents who were exposed to THC had offspring more likely to use heroin.
DADS’ BEHAVIOR COUNTS TOO. Dad’s exposure to THC as an adult also led to offspring who preferred opiates. This was based on epigenetic changes passed on in the sperm. To the extent that this also happens in humans, one could ask how much of the current opiate epidemic is based on parental use of marijuana. Mom’s and dad’s smoking pot could make their offspring more vulnerable to opiate addiction.
Vitamin B6 Plus Lithium Helps Ease Mania Symptoms in Patients With Bipolar Disorder
Daily vitamin B6 (40mg/day), but not B1 (100mg/day), as an adjunctive therapy to lithium was associated with the improvement of mood symptoms in hospitalized patients with bipolar disorder experiencing a manic episode, according to a study published in the Journal of Affective Disorders 2024; 345 103-111: Zandifar et al.
Cannabis and Cannabinoids Don’t Work for Pain or Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
Aaron S. Wolfgang, MD and Charles W. Hoge, MD reviewed data on cannabis in JAMA Psychiatry and found that there were big placebo effects and no evidence for effectiveness of cannabis in military personal.
This negative data, along will all the liability of cannabis potentially causing or triggering psychosis, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia (as well as possibly contributing to cognitive dysfunction, worsening anxiety and depression in patients with mood disorders) makes the use of pot for medical purposes an entirely foolhardy proposition, as well as a waste of money.
Legalization of pot has helped people avoid jail but precipitated a rash of use and over use.
So the bottom line from this editor is: Get Your Priorities Straight. Cannabis and Cannabinoids Don’t Work for Pain or Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and they Worsen Most Everything Else. Save your Money and Do Something Nice for Yourself and Others Instead.

